Sri Mulyani
Food Technology Study Program, Department of Agriculture, Faculty of Animal and Agricultural Sciences, Diponegoro University, Semarang, Indonesia
Rafli Z. Kamil
Food Technology Study Program, Department of Agriculture, Faculty of Animal and Agricultural Sciences, Diponegoro University, Semarang, Indonesia
Brigitta I. Permata
Food Technology Study Program, Department of Agriculture, Faculty of Animal and Agricultural Sciences, Diponegoro University, Semarang, Indonesia
Setya B. M. Abduh
Food Technology Study Program, Department of Agriculture, Faculty of Animal and Agricultural Sciences, Diponegoro University, Semarang, Indonesia
Ahmad N. Al-Baarri
Food Technology Study Program, Department of Agriculture, Faculty of Animal and Agricultural Sciences, Diponegoro University, Semarang, Indonesia
DOI: https://doi.org/10.14456/apst.2025.9
Keywords: Fermentation Lactic acid bacteria Whey cheese Whey product innovation
Abstract
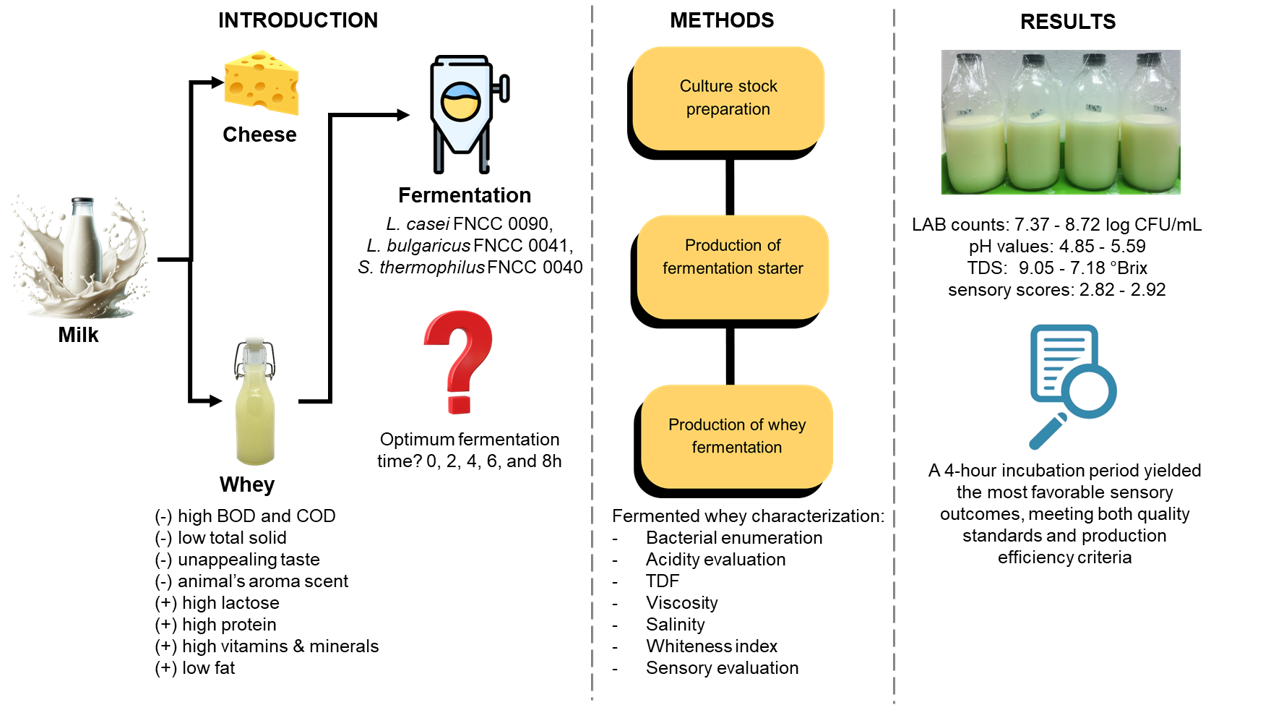
During cheese production, whey is often produced as a by-product with various nutrients content and can cause damage to the environment when not processed appropriately. To reduce its environmental impacts, it is important to develop various methods for processing, such as lactic acid bacterial (LAB) fermentation by using the nutrients content. Therefore, this study aims to use a mixed LAB culture containing Lactobacillus casei FNCC 0090, Lactobacillus bulgaricus FNCC 0041, and Streptococcus thermophilus 0040 for the production of whey beverages. The experiment was carried out with various incubation times of 0, 2, 4, 6, and 8 hours to determine the effect on the products. The variables examined included total dissolved solids (TDS), viscosity, pH, salinity, whiteness index, and total LAB count using the pour-plated method. Subsequently, a sensory evaluation was conducted to evaluate consumer acceptance. The results showed that LAB count ranged from 7.37 to 8.72 log CFU/ml, pH values 4.85 to 5.59, TDS 9.05 to 7.18 °Brix, and sensory scores 2.82 to 2.92. The increase in LAB count correlated with decreased pH, TDS, and salinity, significantly contributing to increased viscosity. However, the incubation period did not affect the whiteness index of whey beverages. Based on the results, a 4-hour incubation period yielded the most favorable sensory outcomes, meeting both quality standards and production efficiency criteria.
How to Cite
Mulyani, S., Kamil, R. Z., Permata, B. I. ., Abduh, S. B. M. ., & Al-Baarri, A. N. . (2025). Fermentation time optimization: Unleashing quality with microbial consortia in whey. Asia-Pacific Journal of Science and Technology, 30(01), APST–30. https://doi.org/10.14456/apst.2025.9
References
Osorio-González CS, N Gómez-Falcon, SK Brar, AA. Cheese whey as a potential feedstock for producing renewable biofuels: a review. Energies. 2022;15:1–15.
Nurhartadi E, A Nursiwi, R Utami, E Widayani. Effect of incubation time and sucrose concentration on probiotic drink characteristic from whey a cheese by-product. J Food Tech. 2018;9:73–83.
Faradila RM, MR Hendratama, NA Rahman. Natural Decomposer from vegetable waste the addition of whey cheese as a source of protein. Atmosphere. 2022;3:32–40.
Mazorra-Manzano MA, Robles-Porchas GR, González-Velázquez DA, Torres-Llanez MJ, Martínez-Porchas M, García-Sifuentes CO, et al. Cheese whey fermentation by its native microbiota: Proteolysis and bioactive peptides release with ACE-inhibitory activity. Fermentation. 2020;6:1–12.
Primurdia EG, J Kusnadi. Antioxidant activity of probiotic drink from dates extract (Phoenic dactilyfera L.) with the isolates of Lactobacillus plantarum and Lactobacillus casei. J Food and Agroind. 2014;2:98–109.
Ma C, A Ma, G Gong, Z Liu, Z Wu, B Guo, Z Chen. Cracking Streptococcus thermophilus to stimulate the growth of the probiotic Lactobacillus casei in co-culture. Intl J Food Microbiology. 2015; 210:42–46
Macwan SR, BK Dabhi, SC Parmar, KD Aparnathi. Whey and its Utilization. Int J Curr Microbiol App Sci. 2016;5:134–155.
Rachman SD, S Djajasoepena, DS Kamara, I Idar, R Sutrisna, A Safari, O Suprijana, S Ishmayana. The quality of yogurt made with a combination of two cultures (Lactobacillus bulgaricus and Streptococcus thermophilus) and three Lactobacillus bacteria. Chimica et Natura Acta. 2015;3:76–79.
Yunivia Y, B Dwiloka, H Rizqiati. Effect of addition of high fructose syrup (HFS) on changes in physicochemical and microbiological properties of green coconut water kefir. J Food Tech. 2018; 3:116–120.
Gao J, X Li, G Zhang, FA Sadiq, J Simal-Gandara, J Xiao, Y Sang. Probiotics in the dairy industry—Advances and opportunities. CRFSFS. 2018;20:3937–3982.
Zuhri R. Effect of starter type of lactic acid bacteria on lactic acid production and protein content in the production of green bean yogurt (Phaseolus radiatus L.). Eduscience Dev J. 2019;1:171–179.
Nurminabari IS, S Sumartini, DPP Arifin. Study of the addition of skim and coconut milk to the characteristics of yoghurt from whey. Pas Food Technol J. 2018;5:54–62.
Liu A, Q Liu, Y Bu, H Hao, T Liu, P Gong, L Zhang, C Chen, H Tian, H Yi. Aroma classification and characterization of Lactobacillus delbrueckii subsp. bulgaricus fermented milk. Food Chem. 2022;15:1–11.
Madureira AR, JC Soares, ME Pintado, AMP Gomes, AC Freitas, MF Xavier. Effect of the incorporation of salted additives on probiotic whey cheeses. Food Biosci. 2015;10:8–17.
Sujono S, MRA Rofat, H Kusuma, K Khotimah. Texture of goat milk yoghurt with different types of starters and length of fermentation. PengabdianMu: J Ilmiah Pengabdian Kepada Masyarakat. 2019;4:55–60.
Blažić M, K Pavić, S Zavadlav, N Marčac. The impact of traditional cheeses and whey on health. Croat J Food Sci Technol. 2017;9:198–203.
Mani-López E, E Palou, ALópez-Malo. Probiotic viability and storage stability of yogurts and fermented milks prepared with several mixtures of lactic acid bacteria. J Dairy Sci. 2014;97:2578–2590.
Kinteki GA, H Rizqiati, A Hintono. Effect on the fermentation duration of goat milk kefir toward hedonic quality, total lactic acid bacteria, total khamir, and pH. J Food Tech. 2018;3:42–50.
Barbosa J, S Borges, M Amorim, MJ Pereira, A Oliveira, ME Pintado, P Teixeira. Comparison of spray drying, freeze drying, and convective hot air drying for the production of a probiotic orange powder. J Funct Foods. 2015;17:340–351.
Agustine L, Y Okfrianti, J Jum. Total Identification of lactic acid bacteria (LAB) in yoghurt with various sucrose and skim milk. J Dunia Gizi. 2018;1:79–83.
Baguna R, A Yelnetty, SE Siswosubroto, N Lontaan. The effect of honey use on pH value, cineresis, and total lactic acid bacteria in sinbiotic yoghurt. Zootec. 2019;40:214–222.
Chavan RS, RC Shraddha, A Kumar, T Nalawade. Whey based beverage: Its functionality, formulations, health benefits and applications. J Food Process Technol. 2015;6:1–8.
Setiarto RHB, N Widhyastuti, I Saskiawan, RM Safitri. The inulin variation concentration effect in fermentation using Lactobacillus acidophilus, Lactobacillus bulgaricus and Streptococcus thermophilus. Biopropal Industyi. 2017;8:1–17.
Bilang M, M Tahir, D Haedar. Study viability encapsulation of probiotic cells (Lactobacillus plantarum and Streptococcus thermophilus) on ice cream. Canrea J: Food Technol Nutr Culinary J. 2018;15:41–52.
Fatmawati F, F Marcelia, Y Badriyah. Effect of moringa leaf extract (Moringa oleifera L.) on yogurt quality. J Indobiosains. 2020;2:21–28.
Tarihoran WC, A Hintono, H Rizqiati. Total of LAB, viscosity, pH, and dissolved solid of buffalo milk kefir with the addition of red dragon fruit (Hylocereus polyrhizus). J Food and Agroind. 2022;10:187–193.
Irawan SA, S Ginting, T Karo-Karo. The effect of physical treatment and storage time on the quality of sugar cane juice. J Rekayasa Pangan dan Pertanian. 2015;3:343–353.
Widagdha S, CF Nisa. The effect of grape juice (Vitis vinifera L.) addition on different fermentation periods toward physic-chemical properties of yogurt. J Food and Agroind. 2015;3:248–258.
Anggraeni L, N Lubis, EC Junaedi. Review: Effect of salt concentration on fermented vegetable products. J Sains Kes. 2021;3:891–899.
Murti RW, S Sumardianto, L Purnamayati. The effect of differences in salt concentration on glutamic acid of rebon shrimp (Acetes sp.) paste. J pengolah has perikan indones. 2021;24:50–59.

Published:
License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
