Suwassa Namvijit
Department of Pharmacy, Faculty of Medicine, Khon Kaen University, Khon Kaen, Thailand
Ajanee Mahakkanukrauh
Department of Medicine, Faculty of Medicine, Khon Kaen University, Khon Kaen, Thailand
Siraphop Suwannaroj
Department of Medicine, Faculty of Medicine, Khon Kaen University, Khon Kaen, Thailand
Patnarin Pongkulkiat
Department of Medicine, Faculty of Medicine, Khon Kaen University, Khon Kaen, Thailand
Tippawan Onchan
Department of Medicine, Faculty of Medicine, Khon Kaen University, Khon Kaen, Thailand
Chingching Foocharoen
Department of Medicine, Faculty of Medicine, Khon Kaen University, Khon Kaen, Thailand
DOI: https://doi.org/10.14456/apst.2025.19
Keywords: systemic sclerosis scleroderma, medication prescription errors prescription modifications prescription cancellations
Abstract
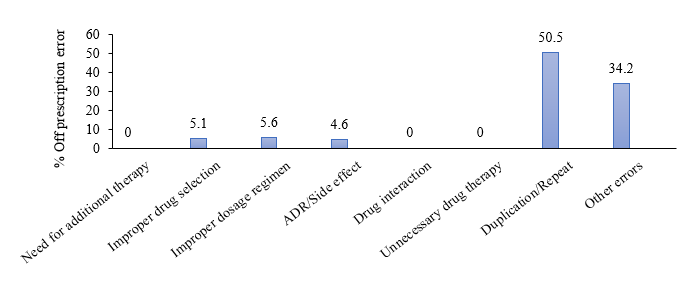
Systemic sclerosis (SSc) is a systemic autoimmune disease characterized by fibrosis, inflammation, and vasculopathy. Treatments aiming to manage all pathologic processes and polypharmacy may inevitably increase the likelihood of prescription errors. We aimed to quantify the numbers of prescription errors and identify factors associated with prescribing errors among SSc patients at the Scleroderma Clinic from January 2016 to December 2022. Prescription error was defined as any modification or cancellation of a medication in the prescription, excluding logistic issues. Among 9,741 prescriptions, 199 (2%) were prescription errors. The most common type of prescription error was duplicated medication (50.5%), followed by prescribed incorrect amount of medicines (34.2%), improper dosage regimen (5.6%), improper drug selection (5.1%) and a history of adverse drug reaction (4.6%). Immunosuppressants and vasodilators were frequently modified and canceled due to their serious side effect history. Neither physician experience nor the types of medication were associated with the occurrence of prescription errors. While the overall rate of prescription errors in the Scleroderma Clinic was low, duplicated medication was the most prevalent type. Implementing strategies targeting these errors could potentially reduce their incidence.
How to Cite
Namvijit, S., Mahakkanukrauh, A., Suwannaroj, S., Pongkulkiat, P. ., Onchan, T., & Foocharoen, C. (2025). Prescription errors in patients with systemic sclerosis: Exploratory data analysis from scleroderma clinic. Asia-Pacific Journal of Science and Technology, 30(02), APST–30. https://doi.org/10.14456/apst.2025.19
References
Stern EP, Denton CP. The pathogenesis of systemic sclerosis. Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 2015;41(3):367–382.
Kowal-Bielecka O, Fransen J, Avouac J, Becker M, Kulak A, Allanore Y, et al. Update of EULAR recommendations for the treatment of systemic sclerosis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2017;76(8):1327–1339.
Alzahrani AA, Alwhaibi MM, Asiri YA, Kamal KM, Alhawassi TM. Description of pharmacists’ reported interventions to prevent prescribing errors among in hospital inpatients: a cross sectional retrospective study. BMC Health Serv Res. 2021;21(1):432.
El Aoufy K, Melis MR, Iovino P, Bambi S, Lorini C, Bonaccorsi G, et al. The rising challenge of poor health literacy of patients with systemic sclerosis: Preliminary data identify important unmet needs in an italian cohort. Nurs Rep. 2024;14(1):556-565.
Shea B, Swinden MV, Tanjong Ghogomu E, Ortiz Z, Katchamart W, Rader T, et al. Folic acid and folinic acid for reducing side effects in patients receiving methotrexate for rheumatoid arthritis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013;2014(5):CD000951.
Bocknek L, Kim T, Spaar P, Russell J, Busog D-N, Howe J, et al. Duplicate medication order errors: Safety gaps and recommendations for improvement. Patient Saf. 2022;4(3):39-47.
Devin J, Cleary BJ and Cullinan S. The impact of health information technology on prescribing errors in hospitals: A systematic review and behaviour change technique analysis. Syst Rev. 2020;9(1):275.
Leviatan I, Oberman B, Zimlichman E, Stein GY. Associations of physicians’ prescribing experience, work hours, and workload with prescription errors. J Am Med Inform Assoc. 2021;28(6):1074–1080.
Hoeve CE, Francisca RDC, Zomerdijk I, Sturkenboom MCJM, Straus SMJM. Description of the risk management of medication errors for centrally authorised products in the european union. Drug Saf. 2020;43(1):45–55.

Published:
License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
