Bee-Hui Yeo
Institute of Bioscience, Universiti Putra Malaysia, Serdang, Malaysia
Oi-Ming Lai
Department of Bioprocess Technology, Faculty of Biotechnology and Biomolecular Sciences, Universiti Putra Malaysia, Serdang, Malaysia.
Teck-Kim Tang
Institute of Bioscience, Universiti Putra Malaysia, Serdang, Malaysia
Shew- Fung Wong
School of Medicine, International Medical University, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia.
Chin-Ping Tan
International Joint Laboratory on Plant Oils Processing and Safety (POPS) JNU-UPM, Department of Food Technology, Faculty of Food Science and Technology, Universiti Putra Malaysia, Serdang, Malaysia.
Yaya Rukayadi
Institute of Bioscience, Universiti Putra Malaysia, Serdang, Malaysia
DOI: https://doi.org/10.14456/apst.2025.65
Keywords: Edible bird’s nest Enzymatic hydrolysis Sialic acid Amino acid profiling Heavy metal contamination
Abstract
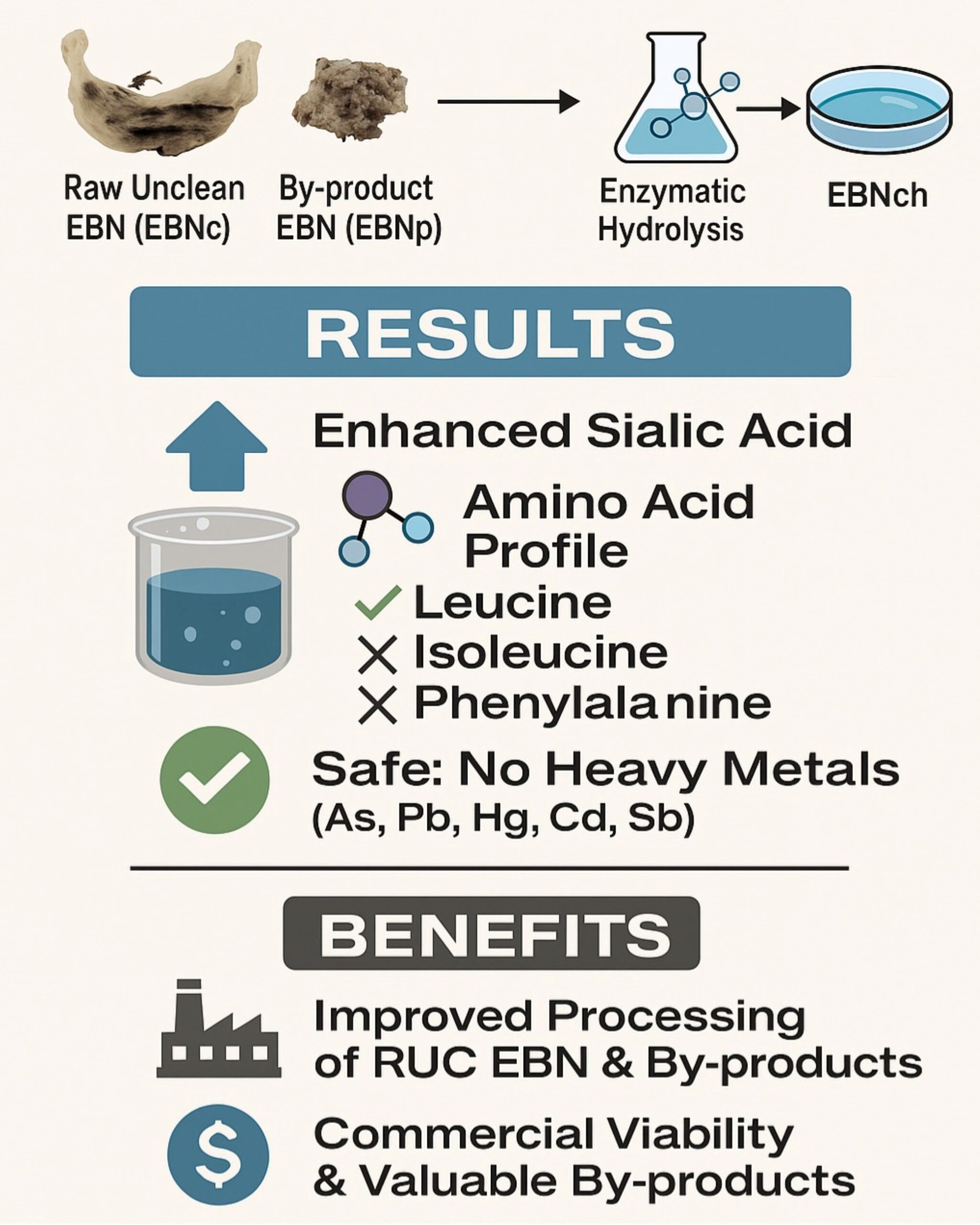
This study examines the impact of enzymatic hydrolysis on the nutritional properties and safety of edible bird’s nest (EBN), particularly focusing on raw unclean (RUC) EBN and by-product EBN. Employing a comparative approach, the research analyzes four samples: two non-hydrolyzed (cup-shaped RUC EBN [EBNc] and by-product of EBN [EBNcp]), and two enzymatically digested (hydrolysate from EBNc [EBNch] and EBNcp [EBNcph]) using bromelain. Nutritional evaluation included measuring sialic acid content, antioxidant activity via DPPH radical scavenging, and amino acid profiling. Results indicated a significant increase in sialic acid content in the hydrolyzed samples (13.97% in EBNch and 14.36% in EBNcph) compared to non-hydrolyzed samples (12.1% in EBNc and 12.3% in EBNcp). Despite a slight reduction in antioxidant activity in hydrolyzed EBNs, they retained substantial antioxidant properties. Amino acid analysis showed the presence of leucine only in hydrolyzed samples, while isoleucine and phenylalanine were exclusive to non-hydrolyzed EBNs. Safety assessments confirmed the absence of heavy metals (arsenic, lead, mercury, cadmium, antimony) in all hydrolysates. Enzymatic hydrolysis significantly enhanced sialic acid content and specific amino acids, maintaining safety standards and proving beneficial for processing heavy feather RUC EBN and by-product EBN, thus improving product recovery and generating valuable by-products. These findings highlight the potential of enzymatic hydrolysis in enhancing the nutritional value and safety of EBN, underscoring its commercial viability.
How to Cite
Yeo, B.-H., Lai, O.-M. ., Tang, T.-K., Wong, S.-. F. ., Tan, C.-P., & Rukayadi, Y. (2025). Comparative evaluation of hydrolyzed vs. un-hydrolyzed edible bird’s nest across raw unclean and by-product grades . Asia-Pacific Journal of Science and Technology, 30(04), APST–30. https://doi.org/10.14456/apst.2025.65
References
Yeo BH, Tang TK, Wong SF, Tan CP, Wang Y, Cheong LZ, Lai OM. Potential residual contaminants in edible bird’s nest. Front Pharmacol. 2021; 12:631136.
Dai Y, Cao J, Wang Y, Chen Y, Jiang L. A comprehensive review of edible bird’s nest. Food Res Int. 2021;140: 109875.
Xu H, Zheng L, Xie Y, Zeng H, Fan Q, Zheng B, Zhang Y. Identification and determination of glycoprotein of edible brid’s nest by nanocomposites based lateral flow immunoassay. Food Control. 2019; 102:214-220.
Lian JM, Fan QY, Li HW. Influence of different processing technology on sialic acid content of edible bird’s nest products. Sci Technol Food Ind. 2017; 38(1):265-268.
Kubala J. Essential Amino Acids: Definition. Benefits and Food Sources. 2018;12.
Quek MC, Chin NL, Yusof YA, Law CL, Tan SW. Characterization of edible bird’s nest of different production, species and geographical origins using nutritional composition, physicochemical properties and antioxidant activities. Food Res Int. 2018; 109:35-43.
Mohamad Nasir NN, Mohamad Ibrahim R, Abu Bakar MZ, Mahmud R, Ab Razak NA. Characterization and Extraction Influence Protein Profiling of Edible Bird’s Nest. Foods. 2021;10(10):2248.
Lee TH, Lee CH, Alia Azmi N, Kavita S, Wong S, Znati M, Ben Jannet H. Characterization of Polar and Non-Polar Compounds of House Edible Bird’s Nest (EBN) from Johor, Malaysia. Chem Biodivers. 2020;17 (1) e201900419.
Zulkifli AS, Babji AS, Lim SJ, Teh AH, Daud NM, Abdul Rahman H. Effect of different hydrolysis time and enzymes on chemical properties, antioxidant and antihyperglycemic activities of edible bird nest hydrolysate. Malaysian Appl Biol. 2019;48(2):149-156.
Babji AS, Etty Syarmila IK, Nur’ Aliah D, Nurul Nadia M, Hadi Akbar D, Norrakiah AS, et al. Assessment on bioactive components of hydrolyzed edible bird nest. Int Food Res J. 2018;25(5):1936-1941.
Elfita L. Analysis on Protein Profile and Amino Acid of Edible Bird’s Nest (Collocalia Fuchiphaga) From Painan. Jurnal Sains Farmasi dan Klinis. 2014;1(1):27-37.
Linh TTM, Son HL, Ai HMM. Nutritional content of vietnamese edible bird’s nest from selected regions. Curr Res Agric Food Sci. 2021; 5:75–81.
Saengkrajang W, Matan N, Matan N. Nutritional composition of the farmed edible bird’s nest (Collocalia fuciphaga) in Thailand. J Food Compos Anal. 2013;31(1):41-45.
Elfita L, Wientarsih I, Sajuthi D, Bachtiar I, Darusman HS. The diversity in nutritional profile of farmed edible bird’s nests from several regions in Indonesia. Biodiversitas. 2020;21(6):2362-2368.
Yao Y. CN107302991A- A kind of formula of bird’s nest jelly and preparation method thereof. Google Patent. 2017.
Li J, Zou F, Chen Y, Fan Q, Huang C, Guo P. CN112042935A- Cubilose concentrated solution and preparation method and application thereof. Google Patent; 2020.
Fan Q, Zeng H, Zhang Y, Zheng B, Lian J. CN112006276A- Brewing type instant cubilose powder and preparation method thereof. Google Patent; 2020.
Hui Yan T, Lim SJ, Babji AS, Rawi MH, Sarbini SR. Enzymatic hydrolysis: Sialylated mucin (SiaMuc) glycoprotein of edible swiftlet’s nest (ESN) and its molecular weight distribution as bioactive ESN SiaMuc-glycopeptide hydrolysate. Int J Biol Macromol. 2020; 175:422-431.
Feng TY, Xue CH, Tong S, Cui HB, Xu J. Determination of sialic acid in edible birds nest using pre-column derivatization reversed phase high performance liquid chromatography with photodiode array or fluorescence detection. Food Sci. 2010;31(8):233-6.
AOAC. Official Method 999.10: Lead, Cadmium, Zinc, Copper, and Iron in Foods. In Official Methods of Analysis of AOAC International (20th ed.). AOAC International; 2016.
AOAC. Official Method 994.12: Determination of amino acids in feeds. J Assoc Official Analytical Chemists. 1998;71(6):171-174.
Ling JWA, Chang LS, Babji AS, Lim SJ. Recovery of value-added glycopeptides from edible bird’s nest (EBN) co-products: enzymatic hydrolysis, physicochemical characteristics and bioactivity. J Sci Food Agric. 2020;100(13):4714-4722.
Ali AAM, Hidayati Syamimi MN, Poh KC, Babji AS, Lim SJ. Comparison of amino acids profile and antioxidant activities between edible bird nest and chicken egg. Malaysian Appl Biol. 2019;48 (2):63-69.
Tang PL, Goh HS, Sia SS. Combined enzymatic hydrolysis and herbal extracts fortification to boost in vitro antioxidant activity of edible bird’s nest solution. Chin Herbal Med. 2021;13(4):549-555.
Tan HY, Sue LM, Lee JL, Lim SJ, Nur’ Aliah D, Babji AS, Sarbini SR. Bioactive sialylated-mucin (SiaMuc) glycopeptide produced from enzymatic hydrolysis of edible swiftlet’s nest (ESN): Degree of hydrolysis, nutritional bioavailability, and physicochemical characteristics. Int J Food Prop. 2022;25(1):252-277.
Chen JXJ, Lim PKC, Wong SF, Mak JW. Determination of the presence and levels of heavy metals and other elements in raw and commercial edible bird nests. Malaysian J Nutr. 2014;20 (3):377-391.
Salim NAA, Othman Z, Harun NA, Moosa S, Omar SA, Azman MA, et al. A preliminary study of elemental characterization for geochemical markers of house and cave edible bird’s nest using naa technique. Jurnal Sains Nuklear Malaysia. 2018;30(1):30-35.
Tan SN, Sani D, Lim CW, Ideris A, Stanslas J, Lim CTS. Proximate Analysis and Safety Profile of Farmed Edible Bird’s Nest in Malaysia and Its Effect on Cancer Cells. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2020; 2020:8068797.
Wahyuni DS, Latif H, Sudarwanto MB, Basri C, Thong D. An investigation of heavy metals in edible bird’s nest from Indonesia using inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. Vet World. 2022;15(2):509-516.
Hamzah Z, Sarojini J, Othman H, Kamarudin H. Waste to wealth for the edible bird nest industry. In: Applied Mechanics and Materials. Trans Tech Publications Ltd. 2015; 754:990-997.

Published:
License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
