Ngoc-Hanh Cao-Luu
Faculty of Chemical Engineering, Can Tho University, Can Tho 900000, Vietnam
Bich-Thuyen Nguyen-Thi
Faculty of Chemical Engineering, Can Tho University, Can Tho 900000, Vietnam
Huynh-Vu-Thanh Luong
Applied Chemical Engineering Laboratory, Faculty of Chemical Engineering, Can Tho University, Can Tho 900000, Vietnam
Lien-Huong Huynh
Faculty of Chemical Engineering, Can Tho University, Can Tho 900000, Vietnam
Thuy-Tien Tiet-Thi
Composite Material Laboratory, Faculty of Chemical Engineering, Can Tho University, Can Tho 900000, Vietnam
Kim-Oanh Nguyen-Thi
Composite Material Laboratory, Faculty of Chemical Engineering, Can Tho University, Can Tho 900000, Vietnam
DOI: https://doi.org/10.14456/apst.2025.36
Keywords: Chitosan Curcumin Electrospinning method Polyvinyl alcohol Wound healing nanofibrous membranes
Abstract
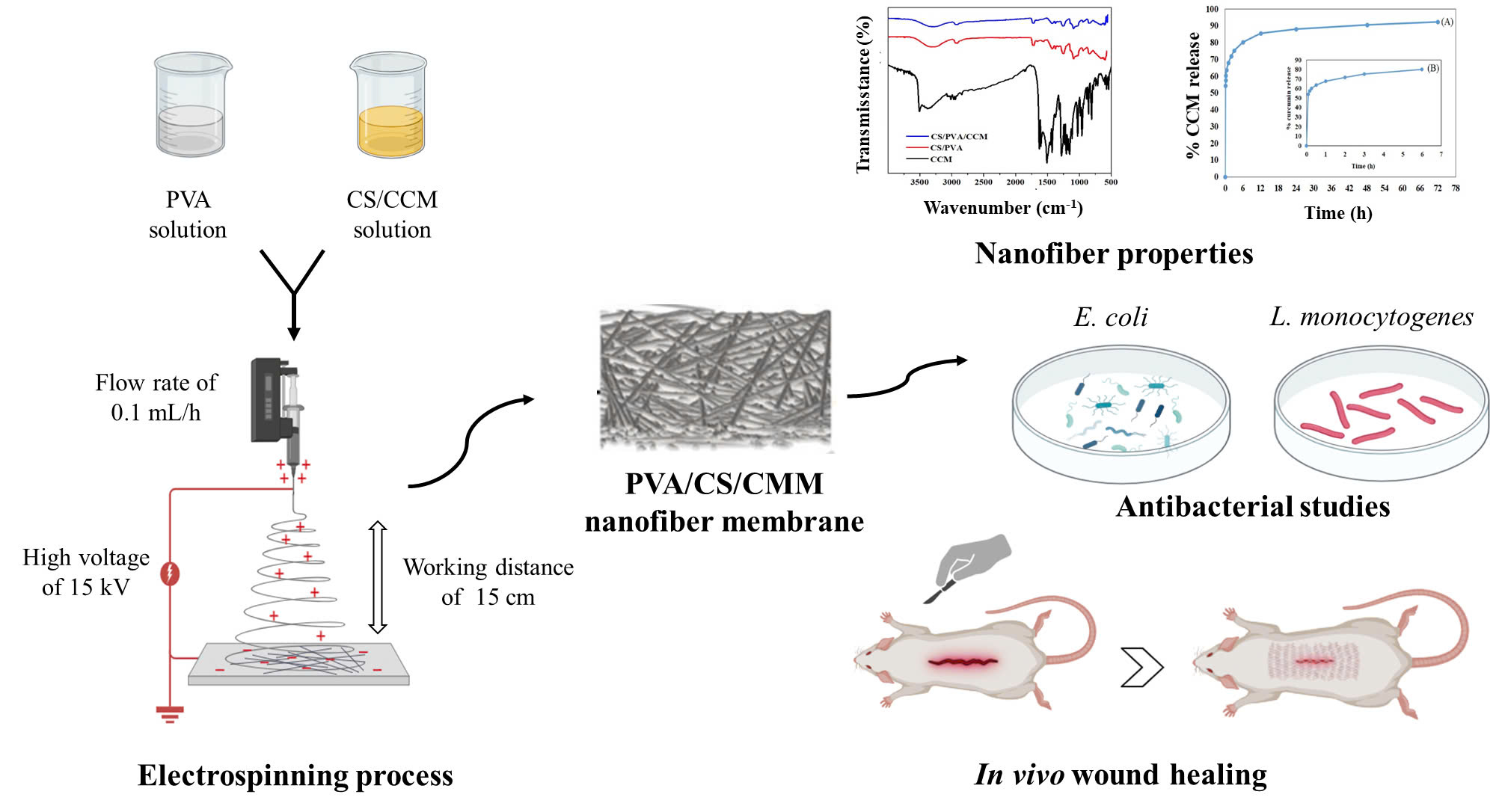
Wound healing nanofiber membranes were successfully fabricated by electrospinning of chitosan (CS) and polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) solution in the presence of curcumin (CCM). As a results, the optimal material parameters included 2% (w/v) for the CS concentration, 8% (w/v) for the PVA concentration, 3% for the CCM concentration (by mass of CS), 3/7 for the CS/PVA volume ratio; the process parameters of 15 cm for the needle tip-to-collector distance, 15 kV for the applied voltage, and 0.1 mL/h for the solution flow rate. The obtained membranes exhibited the relatively uniform diameter fibers distributed from 200 to 450 nm, average diameter at 348.55 ± 51.48 nm, smooth fiber surface, and uniform fiber texture. The fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) results demonstrated the presence of CCM in the CS/PVA/CCM membrane, thereby showing that the structure of CCM is not changed during the fabrication. In-vitro test showed that the amount of CCM released significantly from CS/PVA/CCM membrane during the first 6 hours (up to 80.28%), it was followed by maintain at a rather slow rate, and the maximum CCM released was 92.26% after 72 h. The prepared CCM membrane exhibits high antibacterial activity against Gram-negative (Escherichia coli) and Gram-positive (Listeria monocytogenes) bacteria strain, which is an important property of wound healing membrane. Remarkably, CS/PVA/CCM nanofiber membrane accelabrates healing process in rats with incised wounds and demonstrates superior healing ability comparing to CS/PVA membrane and commercial bandages. In brief, CS/PVA/CCM nanofiber membrane is a potential wound dressing with good healing and high antibacterial properties.
How to Cite
Cao-Luu, N.-H., Nguyen-Thi, B.-T. ., Luong, H.-V.-T. ., Huynh, L.-H. ., Tiet-Thi, T.-T., & Nguyen-Thi, K.-O. (2025). Electrospun chitosan/polyvinyl alcohol nanofibrous membrane loading curcumin to promote wound healing and improve antibacterial properties. Asia-Pacific Journal of Science and Technology, 30(03), APST–30. https://doi.org/10.14456/apst.2025.36
References
Chen K, Hu H, Zeng Y, Pan H, Wang S, Zhang Y, Shi L, Tan G, Pan W, Liu H. Recent advances in electrospun nanofibers for wound dressing. Eur Polym J. 2022;178:111490.
Pereira RF, Barrias CC, Granja PL, Bartolo PJ. Advanced biofabrication strategies for skin regeneration and repair. Nanomedicine. 2013;8(4):603-621.
Zhou S, Xie M, Su J, Cai B, Li J, Zhang K. New insights into balancing wound healing and scarless skin repair. J Tissue Eng. 2023;14.
Liu C, Zhu Y, Lun X, Sheng H, Yan A. Effects of wound dressing based on the combination of silver@ CCM nanoparticles and electrospun CS nanofibers on wound healing. Bioengineered. 2022;13(2): 4328-4339.
Rath G, Hussain T, Chauhan G, Garg T, Goyal AK. Collagen nanofiber containing silver nanoparticles for improved wound-healing applications. J Drug Target. 2016;24(6):520-529.
Croitoru AM, Ficai D, Ficai A, Mihailescu N, Andronescu E, Turculet SC. Nanostructured fibers containing natural or synthetic bioactive compounds in wound dressing applications. Materials. 2020;13(10):2407.
Chen J, Tang X, Wang Z. Techniques for navigating postsurgical adhesions: Insights into mechanisms and future directions. Bioeng Transl Med. 2023;10565.
Gomes SR, Rodrigues G, Martins GG, Roberto MA, Mafra M, Henriques CMR, Silva JC. In vitro and in vivo evaluation of electrospun nanofibers of PCL, CS and gelatin: A comparative study. Mater Sci Eng C. 2015;46:348-358.
Adeli H, Khorasani MT, Parvazinia M. Wound dressing based on electrospun PVA/CS/starch nanofibrous mats: Fabrication, antibacterial and cytocompatibility evaluation and in vitro healing assay. Int J Biol Macromol. 2019;122:238-254.
Matica MA, Aachmann FL, Tøndervik A, Sletta H, Ostafe V. CS as a wound dressing starting material: Antimicrobial properties and mode of action. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(23):5889.
Jana P, Shyam M, Singh S, Jayaprakash V, Dev A. Biodegradable polymers in drug delivery and oral vaccination. Eur Polym J. 2021;142:110155.
Saghazadeh S, Rinoldi C, Schot M, Kashaf SS, Sharifi F, Jalilian E, Khademhosseini A. Drug delivery systems and materials for wound healing applications. Adv Drug Deliver Rev. 2018;127:138-166.
Bi H, Feng T, Li B, Han Y. In Vitro and In Vivo Comparison Study of Electrospun PLA and PLA/PVA/SA Fiber Membranes for Wound Healing. Polymers. 2020;12:839.
Fahimirad S, Abtahi H, Satei P, Ghaznavi-Rad E, Moslehi M, Ganji A. Wound healing performance of PCL/CS based electrospun nanofiber electrosprayed with CCM loaded CS nanoparticles. Carbohydr Polym. 2021;259:117640.
Patrulea V, Ostafe V, Borchard G, Jordan O. CS as a starting material for wound healing applications. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2015;97:417-426.
Biranje S, Madiwale P, Adivarekar RV. Electrospinning of CS/PVA nanofibrous membrane at ultralow solvent concentration. J Polym Res. 2017;24:1-10.
Harpaz D, Axelrod T, Yitian AL, Eltzov E, Marks RS, Tok AI. Dissolvable polyvinyl-alcohol film, a time-barrier to modulate sample flow in a 3D-printed holder for capillary flow paper diagnostics. Materials. 2019;12(3):343.
Peng L, Zhou Y, Lu W, Zhu W, Li Y, Chen K, Zhang G, Xu J, Deng Z, Wang D. Characterization of a novel PVA/CS porous hydrogel combined with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and its application in articular cartilage repair. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2019;20:257.
Nathan KG, Genasan K, Kamarul T. PVA-CS scaffold for tissue engineering and regenerative medicine application: a review. Marine Drugs. 2023;21(5):304.
Chetouani A, Elkolli M, Bounekhel M, Benachour D. CS/oxidized pectin/PVA blend film: Mechanical and biological properties. Polym. Bull. 2017;74:4297–4310.
Fahimirad S, Abtahi H, Satei P, Ghaznavi-Rad E, Moslehi M, Ganji A. Wound healing performance of PCL/CS based electrospun nanofiber electrosprayed with CCM loaded CS nanoparticles. Carbohydr Polym. 2021;259:117640.
Singh H, Dhanka M, Yadav I, Gautam S, Bashir SM, Mishra NC, Hassan S. Technological interventions enhancing CCM bioavailability in wound-healing therapeutics. Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2024;30(2):230-253.
Vivcharenko V, Przekora A. Modifications of wound dressings with bioactive agents to achieve improved pro-healing properties. Appl Sci. 2021;11(9):4114.
Akbik D, Ghadiri M, Chrzanowski W, Rohanizadeh R. CCM as a wound healing agent. Life Sci. 2014;116(1):1-7.
Salehi M, Farzamfar S, Ehterami A, Paknejad Z, Bastami F, Shirian S, Vahedi H, Koehkonan GS, Goodarzi A. Kaolin-loaded CS/PVA electrospun scaffold as a wound dressing material: In vitro and in vivo studies. J Wound Care. 2020;29(5):270-280.
Dhurai B, Saraswathy N, Maheswaran R, Sethupathi P, Vanitha P, Vigneshwaran S, and Rameshbabu V. Electrospinning of CCM loaded CS/poly (lactic acid) nanofilm and evaluation of its medicinal characteristics. Front Mat Sci. 2013;7:350-361.
Li Y, Zhu J, Cheng H, Li G, Cho H, Jiang M, Gao Q, Zhang X. Developments of advanced electrospinning techniques: A critical review. Adv Mater Technol. 2021;6(11):2100410.
Thuy NTT, Ghosh C, Hwang S-G, Lam DT, Park JS. Characteristics of CCM-loaded poly (lactic acid) nanofibers for wound healing. J Mater Sci. 2013;48:7125-7133.
Sedghi R, Shaabani A. Electrospun biocompatible core/shell polymer-free core structure nanofibers with superior antimicrobial potency against multi drug resistance organisms. Polymer. 2016;101:151-157.
Mahmud MM, Zaman S, Perveen A, Jahan RA, Islam MF, Arafat MT. Controlled release of CCM from electrospun fiber mats with antibacterial activity. J Drug Deliv Sci Technol. 2020;55:101386.

Published:
License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
