Saw Mya Soe
Human Movement Sciences, School of Physical Therapy, Faculty of Associated Medical Sciences, Khon Kean University, Khon Kaen, Thailand
Sawitri Wanpen
School of Physical Therapy, Faculty of Associated Medical Sciences, Khon Kean University, Khon Kaen, Thailand
Thiwabhorn Thaweewannakit
School of Physical Therapy, Faculty of Associated Medical Sciences, Khon Kean University, Khon Kaen, Thailand
Punnee Peungsuwan
School of Physical Therapy, Faculty of Associated Medical Sciences, Khon Kean University, Khon Kaen, Thailand
Uraiwan Chatchawan
School of Physical Therapy, Faculty of Associated Medical Sciences, Khon Kean University, Khon Kaen, Thailand
DOI: https://doi.org/10.14456/apst.2025.14
Keywords: Self-Thai foot massage Standard foot care Balance Proprioception
Abstract
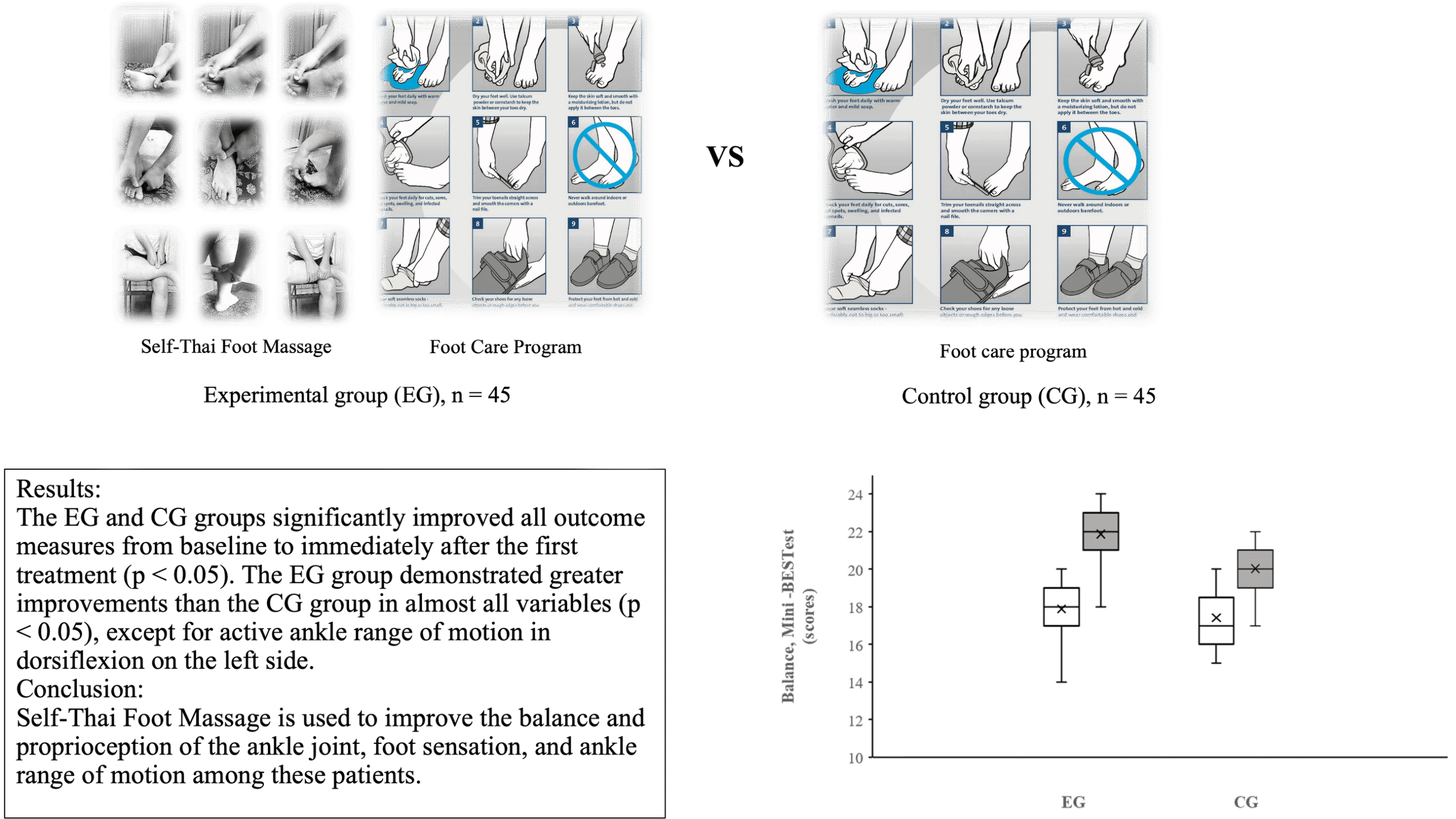
Standard treatments for patients with type 2 diabetes (T2DM) and peripheral neuropathy (DPN) typically include foot care and exercise programs. Self-Thai Foot Massage has been proposed as an alternative therapy for managing this condition. This study investigated the immediate effects of the single intervention of Self-Thai Foot Massage on balance and proprioception of the ankle joint in T2DM with DPN. Ninety patients were recruited and randomly assigned to either the experimental group (EG), receiving Self-Thai Foot Massage and Standard Foot Care, or the comparable group (CG), receiving only Standard Foot Care. Both groups received a single 50-minute treatment. Balance was assessed using the Mini-Balance Evaluation Systems Test (MBT), ankle joint proprioception was measured using the Ankle Joint Proprioception (JPS) test, foot sensation was evaluated using the Semmes-Weinstein Monofilament Test (SWMT), and the active/passive range of motion of the ankle was measured using the Kinovea program, both before and immediately after a single treatment. The independent t-tests and Two-sample Mann-Whitney tests were used to compare post-treatment data between treatment groups. The EG and CG groups showed significant improvements in all outcome measures from baseline to immediately after the first treatment (p<0.05). The EG group demonstrated greater improvements than the CG group in almost all variables (p<0.05), except for active ankle range of motion in dorsiflexion on the left side. This study highlights the potential benefits of Self-Thai Foot Massage for immediate improvements in balance and proprioception of ankle joint, foot sensation, and ankle range of motion among these patients.
How to Cite
Saw Mya Soe, Wanpen, S., Thaweewannakit, T., Peungsuwan, P., & Chatchawan, U. (2025). Immediate Effect of Self-Thai Foot Massage (STFM) on Balance and Ankle Joint Proprioception in Type II Diabetic Patients with Peripheral Neuropathy (DPN): A Single-Blind Randomized Controlled Trial. Asia-Pacific Journal of Science and Technology, 30(01), APST–30. https://doi.org/10.14456/apst.2025.14
References
Hicks CW, Selvin E. Epidemiology of peripheral neuropathy and lower extremity disease in diabetes. Curr Diab Rep. 2019;19(86):1-8.
Hewston P, Deshpande N. Falls and balance impairments in older adults with type 2 diabetes: thinking beyond diabetic peripheral neuropathy. Can J Diabetes. 2016;40(1):6-9.
Win MM, Fukai K, Nyunt HH, Hyodo Y, Linn KZ. Prevalence of peripheral neuropathy and its impact on activities of daily living in people with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Nurs Health Sci. 2019;21(4):445-453.
Schulte L, Roberts MS, Zimmerman C, Ketler J, Simon LS. A quantitative assessment of limited joint mobility in patients with diabetes. Arthritis Rheum. 1993;36(10):1429-1443.
Mecagni C, Smith JP, Roberts KE, O’Sullivan SB. Balance and ankle range of motion in community-dwelling women aged 64 to 87 years: a correlational study. Phys Ther. 2000;80(10):1004-1011.
Lim KB, Kim DJ, Noh JH, Yoo J, Moon JW. Comparison of balance ability between patients with type 2 diabetes and with and without peripheral neuropathy. PM&R. 2014;6(3):209-214.
Timar B, Timar R, Gaiță L, Oancea C, Levai C, Lungeanu D. The impact of diabetic neuropathy on balance and on the risk of falls in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a cross-sectional study. PloS one. 2016;11(4):1-11.
American Diabetes Association Position Statement: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes—2015. Diabetes Care 2015;38(Suppl. 1):S1–S94.
Chatchawan U, Eungpinichpong W, Plandee P, Yamauchi J. Effects of Thai foot massage on balance performance in diabetic patients with peripheral neuropathy: a randomized parallel-controlled trial. Med Sci Monit Basic Res. 2015;21:67-75.
Vaillant J, Rouland A, Martigné P, Braujou R, Nissen MJ, Caillat-Miousse JL, et al. Massage and mobilization of the feet and ankles in elderly adults: effect on clinical balance performance. Man Ther. 2009;14(6):661-664.
Chatchawan U, Jarasrungsichol K, Yamauchi J. Immediate effects of Self-Thai Foot Massage on skin blood flow, skin temperature, and range of motion of the foot and ankle in type 2 diabetic patients. J Altern Complement Med. 2020;26(6):491-500.
Franchignoni F, Horak F, Godi M, Nardone A, Giordano A. Using psychometric techniques to improve the Balance Evaluation Systems Test: the mini-BESTest. J Rehabil Med. 2010;42(4):323-331.
Sibley KM, Beauchamp MK, Van Ooteghem K, Straus SE, Jaglal SB. Using the systems framework for postural control to analyze the components of balance evaluated in standardized balance measures: a scoping review. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2015;96(1):122-132.
Phyu SN, Peungsuwan P, Puntumetakul R, Chatchawan U. Reliability, and validity of mini-balance evaluation system test in type 2 diabetic patients with peripheral neuropathy. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022;19(11):6944.
Phyu SN, Wanpen S, Chatchawan U. Responsiveness of the Mini-Balance evaluation system test in type 2 Diabetic patients with Peripheral Neuropathy. J Multidiscip Res. 2022;15:3015-3028.
Marques A, Silva A, Oliveira A, Cruz J, Machado A, Jácome C. Validity and relative ability of 4 balance tests to identify fall status of older adults with type 2 diabetes. J Geriatr Phys Ther. 2017;40(4):227-232.
de Mettelinge TR, Delbaere K, Calders P, Gysel T, Van Den Noortgate N, Cambier D. The impact of peripheral neuropathy and cognitive decrements on gait in older adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2013;94(6):1074-1079.
Godi M, Franchignoni F, Caligari M, Giordano A, Turcato AM, Nardone A. Comparison of reliability, validity, and responsiveness of the mini-BESTest and Berg Balance Scale in patients with balance disorders. Phys Ther. 2013;93(2):158-167.
Borm GF, Fransen J, Lemmens WA. A simple sample size formula for analysis of covariance in randomized clinical trials. J Clin Epidemiol. 2007;60(12):1234-1238.
Sucharit W, Eungpinichpong W, Hunsawong T, Pungsuwan P, Bennett S, Hojo E, et al. Pre- and post-treatment study of the application of a traditional Thai massage protocol for treating office syndrome. Asia Pac J Sci Technol. 2023;28(03):1-9.
Sucharit W, Roberts N, Eungpinichpong W, Hunsawong T, Chatchawan U. Standardised 25-step traditional Thai massage (TTM) protocol for treating Office Syndrome (OS). Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023;20(12):1-16.
Howarth D. Preventing foot complications in people with diabetes mellitus. Nurs Stand. 2019;34(7):69-74.
Allet L, Armand S, De Bie RA, Golay A, Monnin D, Aminian K, et al. The gait and balance of patients with diabetes can be improved: a randomised controlled trial. Diabetologia. 2010;53:458-466.
Houten D, Cooper D. How does cryotherapy effect ankle proprioception in healthy individuals?. Somatosens Mot Res. 2017;34(3):158-171.
Venturni C, Venturni A, Venturni V. Reliability of a universal goniometer in assessing active ankle dorsiflexion and plantar flexion range of motion in healthy male athletes. J Athl Train. 2006;41(4):425-429.
Nather A, Neo SH, Chionh SB, Liew SC, Sim EY, Chew JL. Assessment of sensory neuropathy in diabetic patients without diabetic foot problems. J Diabetes Complications. 2008;22(2):126-131.
Feng Y, Schlösser FJ, Sumpio BE. The Semmes Weinstein monofilament examination as a screening tool for diabetic peripheral neuropathy. J Vasc Surg. 2009;50(3):675-682.
Guzmán-Valdivia CH, Blanco-Ortega A, Oliver-Salazar MA, Carrera-Escobedo JL. Therapeutic motion analysis of lower limbs using Kinovea. Int J Soft Comput Eng. 2013;3(2):2231-2307.
Picot B, Dury J, Néron G, Samozino P, Terrier R, Rémy-Neris O, et al. Validity and reliability of video analysis to evaluate ankle proprioceptive reintegration during postural control. Gait Posture. 2022;91:155-160.
Eugpinichpong W, Montri N. Basic physiological effects of modified foot massage. J Med Tech Phys Ther. 1999;11(3):98-105.
Vaillant J, Vuillerme N, Janvey A, Louis F, Braujou R, Juvin R, et al. Effect of manipulation of the feet and ankles on postural control in elderly adults. Brain Res Bull. 2008;75(1):18-22.
Charkhkar H, Shell CE, Marasco PD, Pinault GJ, Tyler DJ, Triolo RJ. High-density peripheral nerve cuffs restore natural sensation to individuals with lower-limb amputations. J Neural Eng. 2018;15(5):1-16.
Hamidi H, Shojaedin S, Letafatkar A. Efficacy of the reflexology and Yumeiho therapy massages on lower limb pain and balance in women with diabetic neuropathy. J Gorgan Univ Med Sci. 2016;18(2):61-68.
Siva Kumar AV, Lahari AKS, Maruthy KN, Kareem SK, MaheshKumar, K. Effects of Therapeutic Calf Massage on Cardiac Autonomic Function in Healthy Volunteers-a Pilot Study. Int J Ther Massage Bodywork. 2023;16(1):24-29.
Whatley J, Perkins J, Samuel C. Reflexology: exploring the mechanism of action. Complement Ther Clin Pract. 2022;48:1-7.
Field T, Diego M, Hernandez-Rief M. Massage therapy research. Dev Rev. 2007;27(1):75-89.

Published:
License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
