Mohamed I Abou-Dobara
Department of Botany and Microbiology, Faculty of Science, Damietta University, New Damietta, Egypt
Zakaria AM Baka
Department of Botany and Microbiology, Faculty of Science, Damietta University, New Damietta, Egypt
Shimaa M El-Salamony
Department of Botany and Microbiology, Faculty of Science, Damietta University, New Damietta, Egypt
Mohamed M El-Zahed
Department of Botany and Microbiology, Faculty of Science, Damietta University, New Damietta, Egypt
Keywords: Anticandidal activity, Bacillus licheniformis, Nanocomposite, Vancomycin, ZnO NPs
Abstract
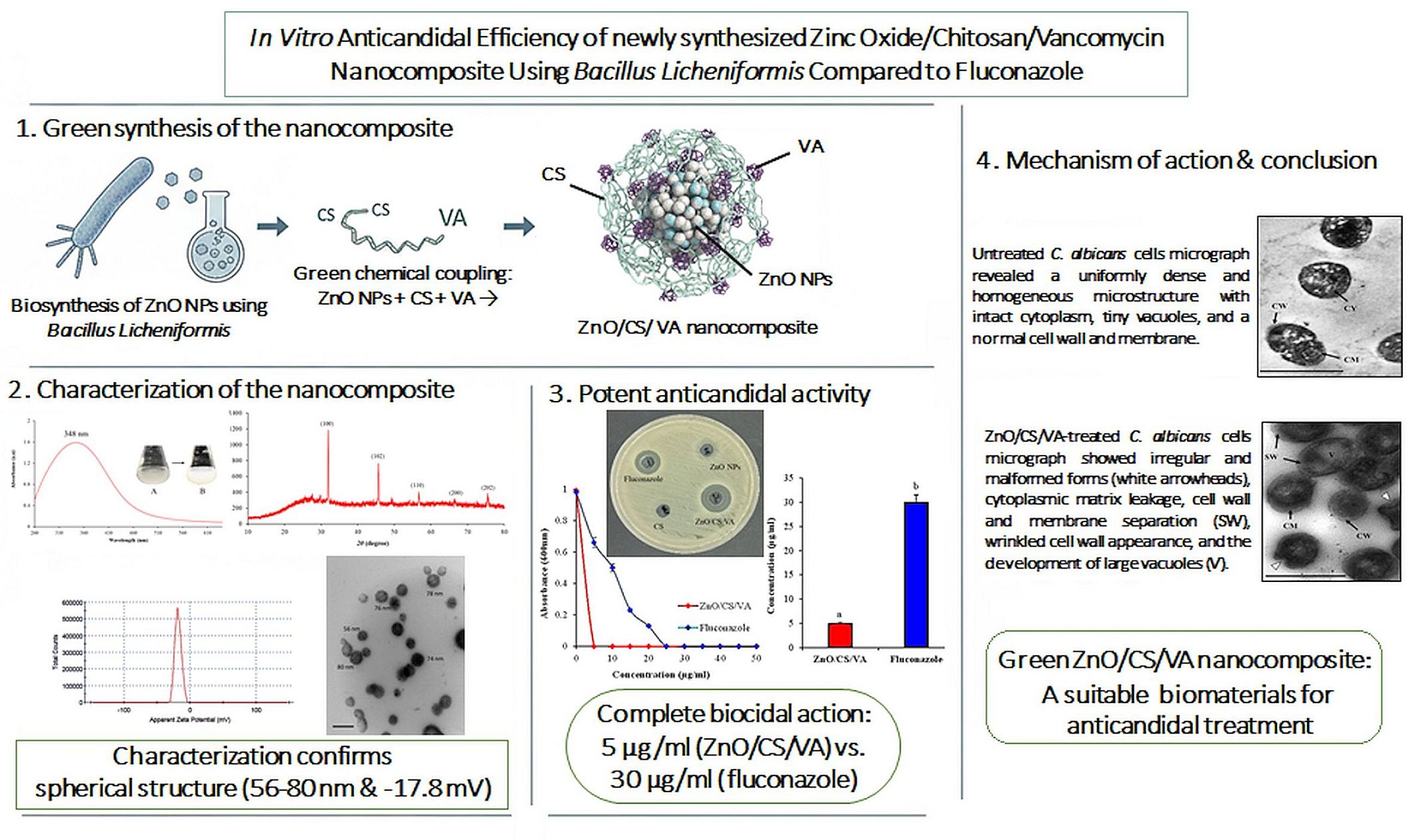
The zinc oxide/chitosan nanocomposite functionalized with vancomycin (ZnO/CS/VA), which acts as a novel anticandidal modifier, was prepared using an environmentally friendly technique. Zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnO NPs) were biosynthesized using Bacillus licheniformis ATCC 4527 and then linked to chitosan (CS) and vancomycin (VA) through a green chemical method. Several methods were utilized to characterize the prepared nanocomposite. UV-Vis spectroscopy results indicated an absorption peak at 348 nm. Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) and X-ray diffractometer (XRD) analyses demonstrated that the material matrix of the nanocomposite included ZnO NPs and various active groups. Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) images showed that the ZnO/CS/VA nanocomposite was spherical-shaped with a size range of 56-80 nm. The anticandidal effect of ZnO/CS/VA, used as a modifier to enhance antimicrobial activity, was tested against Candida albicans ATCC 10231. ZnO/CS/VA exhibited significant anticandidal activity in the agar well-diffusion test, minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC), and minimum fungicidal concentration (MFC) compared to the standard drug fluconazole. As the ZnO/CS/VA dose and the anticandidal inhibition increased, the antimicrobial activity became reliant on the nanocomposite dose. Five μg/mL was enough to cause complete biocidal action against Candida albicans, while 25 μg/mL of fluconazole was required. TEM micrographs of ZnO/CS/VA-treated Candida albicans showed various malformations and distortions in cell structure, including damage to the cell wall and the presence of vacuoles, indicating its potent antimicrobial effects. The results suggest that the combination of zinc oxide/chitosan nanocomposite and vancomycin could serve as an effective biomaterial for antifungal treatment and other medical applications.
References
Monaco A, Caruso M, Bellantuono L, Cazzolla Gatti R, Fania A, Lacalamita A. Measuring water pollution effects on antimicrobial resistance through explainable artificial intelligence. Environ Pollut. 2025;367:125620.
Ayukekbong JA, Ntemgwa M, Atabe AN. The threat of antimicrobial resistance in developing countries: Causes and control strategies. Antimicrob Resist Infect Control. 2017;6(1):47-49.
Ranjbar R, Alam M. Global burden of bacterial antimicrobial resistance in 2019: A systematic analysis. EBN. 2024;27:16-22.
Walsh TR, Gales AC, Laxminarayan R, Dodd PC. Antimicrobial resistance: Addressing a global threat to humanity. PLOS Med. 2023;20(7):e1004264.
Kennedy MJ, Volz PA. Ecology of Candida albicans gut colonization: Inhibition of Candida adhesion, colonization, and dissemination from the gastrointestinal tract by bacterial antagonism. Infect Immun. 1985;49(3):654–663.
Ghosh M, Mandal S, Roy A, Chakrabarty S, Chakrabarti G, Pradhan SK. Enhanced antifungal activity of fluconazole conjugated with Cu-Ag-ZnO nanocomposite. Mater Sci Eng C. 2020;106:110160.
Abou-Dobara MI, Kamel MA, El-Sayed AKA, El-Zahed MM. Antibacterial activity of extracellular biosynthesized iron oxide nanoparticles against locally isolated β-lactamase-producing Escherichia coli from Egypt. Discov Appl Sci. 2024;6(3):113-115.
El-Fawal M, A. El-Fallal A, I. Abou-Dobara M, K.A. El-Sayed A, El-Zahed MM. Preparation, characterization, and antibacterial activity of newly biosynthesized ampicillin/chitosan/selenium nanocomposite (AMP/CS/SENC) using Fusarium fujikuroi PP794203 against multidrug-resistant Escherichia coli PP797596. J Microbiol Biotechnol Food Sci. 2024;14(3):e11608.
El-Harairey MA, Saad HR, Moawed EA, Elafndi RK, Eissa MS, El Zahed MM, et al. Evaluation of titanium dioxide/catechol polyurethane composite for antimicrobial resistance and wastewater treatment. Discov Mater. 2024;4(1):66-69.
El-Zahed MM, Abou-Dobara MI, El-Khodary MM, Mousa MMA. Antimicrobial activity and nanoremediation of heavy metals using biosynthesized CS/GO/ZnO nanocomposite by Bacillus subtilis ATCC 6633 alone or immobilized in a macroporous cryogel. Microb Cell Fact. 2024;23(1):278-281.
El-Fallal AA, Abou-Dobara MI, El-Sayed AKA, El-Fawal MF, El-Zahed MM. Green synthesis, optimization and antifungal activity of Se NPs using Fusarium fujikuroi MED14. Sci J Damietta Fac Sci. 2024;14(3):57–65.
Fayed RM, Mohamed Baka ZA, Farouk BH, El-Zahed MM. Antibacterial and cytotoxic activities of a newly green synthesized ZnO/Se nanocomposite combined with Washingtonia robusta H. Wendl fruit extract. Biocatal Agric Biotechnol. 2025;64:103500.
Majumder DD, Banerjee R, Ulrichs CH, Mewis I, Goswami A. Nano-materials: Science of bottom-up and top-down. IETE Technical Review. 2007;24(1):9–25.
Mohamed EA, El Zahed MM. Anticandidal applications of selenium nanoparticles biosynthesized with Limosilactobacillus fermentum (OR553490). Discover Nano. 2024;19(1):115-120.
Fayed RM, Elnemr AM, El-Zahed MM. Synthesis, characterization, antimicrobial and electrochemical studies of biosynthesized zinc oxide nanoparticles using the probiotic Bacillus coagulans (ATCC 7050). J Microbiol Biotechnol Food Sci. 2023;13(3):e9962.
Abd El-Nour AT, Abou-Dobara MI, El-Sayed AKA, El-Zahed MM. Extracellular biosynthesis and antimicrobial activity of Bacillus subtilis ATCC 6633 zinc oxide nanoparticles. Sci J Damietta Fac Sci. 2023;13(2):39–47.
Todorov SD, Ivanova IV, Popov I, Weeks R, Chikindas ML. Bacillus spore-forming probiotics: Benefits with concerns. Crit Rev Microbiol. 2022;48(4):513–530.
Abinaya M, Vaseeharan B, Divya M, Sharmili A, Govindarajan M, Alharbi NS, et al. Bacterial exopolysaccharide (EPS)-coated ZnO nanoparticles showed high antibiofilm activity and larvicidal toxicity against malaria and Zika virus vectors. J Trace Elem Med Biol. 2018;45:93–103.
Gomaa EZ. Microbial mediated synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles, characterization and multifaceted applications. J Inorg Organomet Polym Mater. 2022;32(11):4114–4132.
El-Fallal AA, Elfayoumy RA, El-Zahed MM. Antibacterial activity of biosynthesized zinc oxide nanoparticles using Kombucha extract. SN Appl Sci. 2023;5(12):332-335.
Abd El-Nour AT, Abou-Dobara MI, El-Sayed AKA, El-Zahed MM. Antibacterial activity of optimized extracellular biosynthesized zinc oxide nanoparticles using Corynebacterium sp. ATCC 6931. SJDFS. 2023;13(3):63–70.
El Zahed MM, Eissa MS, Moawed EA, El Sadda RR. Application of thiourea polyurethane foam/zinc oxide nanocomposite for anticancer effects and antimicrobial potential. Discov Appl Sci. 2024;6(3):112-116.
Fayed RM, Baka ZA, El-Zahed MM. Antibacterial activity of green synthesized zinc oxide nanoparticles using Washingtonia robusta H. Wendl fruit extract. SJDFS. 2024;14(3):90–101.
Ahmadpour Kermani S, Salari S, Ghasemi Nejad Almani P. Comparison of antifungal and cytotoxicity activities of titanium dioxide and zinc oxide nanoparticles with amphotericin B against different Candida species: In vitro evaluation. J Clin Lab Anal. 2021;35(1):e23577.
Zhang R, Carlsson F, Edman M, Hummelgård M, Jonsson BG, Bylund D, et al. Escherichia coli bacteria develop adaptive resistance to antibacterial ZnO nanoparticles. Adv Biosyst. 2018;2(5):1800019.
CLSI (Clinical and Laboratory Standards). 27th edition. Performance standards for antimicrobial susceptibility testing. Performance standards for antimicrobial susceptibility testing: Approved standard- twenty-seven Edition. CLSI, Wayne, PA; 2017.
CLSI. (Clinical and Laboratory Standards). 7th edition. Reference method for broth dilution antifungal susceptibility testing of yeasts; approved standard M27-A3. CLSI, Wayne, PA; 2008.
Markus J, Mathiyalagan R, Kim YJ, Abbai R, Singh P, Ahn S, et al. Intracellular synthesis of gold nanoparticles with antioxidant activity by probiotic Lactobacillus kimchicus DCY51T isolated from Korean kimchi. Enzyme Microb Technol. 2016;95:85–93.
Ali SA, Ali ES, Hamdy G, Badawy MSEM, Ismail AR, El-Sabbagh InasA. Enhancing physical characteristics and antibacterial efficacy of chitosan through investigation of microwave-assisted chemically formulated chitosan-coated ZnO and chitosan/ZnO physical composite. Sci Rep. 2024;14(1):9348.
Salman JAS, Kadhim AA, Haider AJ. Biosynthesis, characterization and antibacterial effect of ZnO nanoparticles synthesized by Lactobacillus Spp. J Global Pharma Technol. 2018;10(03):348–55.
Fozouni L, Tahaei M. Anticandidal effects of zinc oxide nanoparticles on fluconazole-resistant Candida isolates causing diarrhea in calves, in vitro. Archives of Razi Institute. 2023;78(1):499-501.
Sirelkhatim A, Mahmud S, Seeni A, Kaus NHM, Ann LC, Bakhori SKM. Review on zinc oxide nanoparticles: Antibacterial activity and toxicity mechanism. Nanomicro Lett. 2015;7(3):219–242.
Mehta M, Allen-Gipson D, Mohapatra S, Kindy M, Limayem A. Study on the therapeutic index and synergistic effect of chitosan-zinc oxide nanomicellar composites for drug-resistant bacterial biofilm inhibition. Int J Pharm. 2019;565:472–480.
Iqtedar M, Riaz H, Kaleem A, Abdullah R, Aihetasham A, Naz S. Biosynthesis, optimization and characterization of ZnO nanoparticles using Bacillus cereus MN181367 and their antimicrobial activity against multidrug resistant bacteria. Rev Mex Ing Quim. 2020;19:253–266.
Aung KK, Htun KT. Preparations and characterizations of chitosan, ZnO nanoparticle and chitosan-ZnO nanocomposite. J Myanmar Acad Arts Sci. 2020;18:247-258.

License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
