Yupaporn Phannarangsee
Department of Biotechnology, Faculty of Technology, Khon Kaen University, Khon Kaen, Thailand
Haruthairat Kitwetcharoen
Department of Biotechnology, Faculty of Technology, Khon Kaen University, Khon Kaen, Thailand
Sudarat Thanonkeo
Walai Rukhavej Botanical Research Institute (WRBRI), Mahasarakham University, Maha Sarakham, Thailand
Preekamol Klanrit
Department of Biotechnology, Faculty of Technology, Khon Kaen University, Khon Kaen, Thailand
Mamoru Yamada
Research Center for Thermotolerant Microbial Resources, Yamaguchi University, Yamaguchi, Japan
Pornthap Thanonkeo
Department of Biotechnology, Faculty of Technology, Khon Kaen University, Khon Kaen, Thailand
DOI: https://doi.org/10.14456/apst.2025.27
Keywords: Ethanologenic fermentative bacteria Genetic engineering Molecular cloning Stress-responsive proteins Zymomonas mobilis
Abstract
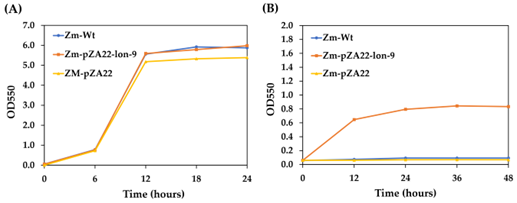
The Lon protease plays a crucial role in bacterial genome stability and cellular homeostasis under various stress conditions. In this study, the lon gene encoding the Lon protease in Zymomonas mobilis TISTR548 was cloned and characterized, and its overexpression in Z. mobilis cells was evaluated. The lon gene had an open reading frame of 2,427 bp, encoding 809 amino acid residues with a relative molecular weight of 89 kDa and a predicted isoelectric point (pI) of 6.42. The Lon protease of Z. mobilis shared several conserved structural and functional features with other Lon proteases. Overexpression of the lon gene improved bacterial cell growth under heat stress at 40.5°C and ethanol toxicity at 10% (v/v). Furthermore, it helped bacterial cells maintain a regular rod shape under stressful conditions, suggesting a role in the cell division mechanism. These findings are valuable for future efforts to improve Z. mobilis strains for enhanced tolerance to heat, ethanol, and other stressful conditions. The successful cloning, expression, and characterization of the Lon protease gene provide insights into the role of this important protein in the stress response and cell division of Z. mobilis
How to Cite
Phannarangsee, Y., Kitwetcharoen, H., Thanonkeo, S., Klanrit, P., Yamada, M., & Thanonkeo, P. (2025). Overexpression of the lon protease and its impact on heat and ethanol stress tolerance in Z. mobilis. Asia-Pacific Journal of Science and Technology, 30(02), APST–30. https://doi.org/10.14456/apst.2025.27
References
Gottesman S. Proteolysis in bacterial regulatory circuits. Annu Rev Cell Dev Bi. 2003;19:565–587.
Burton RE, Baker TA, Sauer RT. Nucleotide-dependent substrate recognition by the AAA+ HslUV protease. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2005;12(3):245–251.
Kannan G, Wilks, JC, Fitzgerald DM, Jones, BD, Bon Durant SS, Slonczewski JL. Rapid acid treatment of Escherichia coli: Transcriptomic response and recovery. BMC Microbiol. 2008;8(1):1–13.
Khattar MM. Overexpression of the hslVU operon suppresses SOS-mediated inhibition of cell division in Escherichia coli. FEBS Lett. 1997;414(2):402–404.
Schweder T, Lee KH. Lomovskaya O, Matin A. Regulation of Escherichia coli starvation sigma factor (sigma s) by ClpXP protease. J. Bacteriol. 1996;178(2):470-476.
Frees D, Qazi, SNA, Hill PJ, Ingmer H. Alternative roles of ClpX and ClpP in Staphylococcus aureus stress tolerance and virulence. Mol Microbiol. 2003;48(6):1565–1578.
Jenal U, Hengge-Aronis R. Regulation by proteolysis in bacterial cells. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2003;6(2):163–172.
Nicoloff H, Perreten V, Levy SB. Increased genome instability in Escherichia coli lon: relation to emergence of multiple-antibiotic-resistant (Mar) mutants caused by insertion sequence elements and large tandem genomic amplifications. Antimicrob Agents Ch. 2007;51(4):1293–1303.
Jonas K, Liu J, Chien P, Laub MT. Proteotoxic stress induces a cell-cycle arrest by stimulating Lon to degrade the replication initiator DnaA. Cell. 2013;154(3):623–636.
Leslie DJ, Heinen C, Schramm FD, Thüring M, Aakre CD, Murray SM, Jonas K. Nutritional control of DNA replication initiation through the proteolysis and regulated translation of DnaA. PLoS Genet. 2015;11(7):1-25.
Gross MH, Konieczny I. Polyphosphate induces the proteolysis of ADP-bound fraction of initiator to inhibit DNA replication initiation upon stress in Escherichia coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020;48(10):5457–5466.
Xie F, Li G, Zhang Y, Zhou, L, Liu S, Liu S, Wang C. The Lon protease homologue LonA, not LonC, contributes to the stress tolerance and biofilm formation of Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae. Microb Pathogenesis. 2016;93:38–43.
Thanonkeo P, Sootsuwan K, Leelavacharamas V, Yamada M. Cloning and transcriptional analysis of groES and groEL in ethanol-producing bacterium Zymomonas mobilis TISTR 548. Pak J Biol Sci. 2007;10(1):13–22.
Misawa N, Okamoto T, Nakamura K, Kitamura K, Yanase H, Tonomura K. Construction of a new shuttle vector for Zymomonas mobilis. Agric Biol Chem. 1986;50(12):3201-3203.
Sambrook J, Fritsch ER, Maniatis T. Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual (2nd ed.). Cold Spring Harbor, NY: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press; 1989.
Sambrook J, Russell DW. Preparation and transformation of competent E. coli using calcium chloride. CSH Protoc. 2006;2006(1):pdb.prot3932.
Anggarini S, Murata M, Kido K, Kosaka T, Sootsuwan K, Thanonkeo, P, Yamada M. Improvement of thermotolerance of Zymomonas mobilis by genes for reactive oxygen species-scavenging enzymes and heat shock proteins. Front Microbiol. 2020;10:1-14.
Okamoto T, Nakamura K. Simple and highly efficient transformation method for Zymomonas mobilis: electroporation. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 1992;56:833-833.
Kirthika P, Lloren KKS, Jawalagatti V, Lee JH. Structure, substrate specificity and role of Lon protease in bacterial pathogenesis and survival. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(4):1-13.
Tzeng SR, Tseng YC, Lin CC, Hsu CY, Huang SJ, Kuo YT, Chang CI. Molecular insights into substrate recognition and discrimination by the N-terminal domain of lon AAA+ protease. Elife. 2021;10:1-23.
Coscia F, Löwe J. Cryo-EM structure of the full-length Lon protease from Thermus thermophilus. FEBS Lett. 2021;595(21):2691–2700.
Gur E. Vishkautzan M, Sauer RT. Protein unfolding and degradation by the AAA+ Lon protease. Protein Sci. 2012;21(2):268–278.
Voos W, Pollecker K. The mitochondrial Lon protease: Novel functions off the beaten track?. Biomolecules. 2020;10(2):1-17.
García-Nafría J, Ondrovičová G, Blagova E, Levdikov VM, Bauer JA, Suzuki CK, et al. Structure of the catalytic domain of the human mitochondrial Lon protease: Proposed relation of oligomer formation and activity. Protein Sci. 2010;19(5):987–999.
Samappito J, Yamada M, Klanrit P, Thanonkeo P. Characterization of a thermo-adapted strain of Zymomonas mobilis for ethanol production at high temperature. 3 Biotech. 2018;8(11):1-9.
Kosaka T, Nishioka A, Sakurada T, Miura K, Anggarini S, Yamada M. Enhancement of thermal resistance by metal ions in thermotolerant Zymomonas mobilis TISTR 548. Front Microbiol. 2020;11:1-10.
Figaj D, Czaplewska P, Przepióra T, Ambroziak P, Potrykus M, Skorko-Glonek J. Lon protease is important for growth under stressful conditions and pathogenicity of the phytopathogen, bacterium Dickeya solani. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(10):1-30.
Liao JH, Kuo CI, Huang YY, Lin YC, Lin YC, Yang CY, et al. A Lon-like protease with no ATP-powered unfolding activity. PLoS One. 2012;7(7):e40226.
Riethdorf S, Volker U, Gerth U, Winkler A, Engelmann S, Hecker, M. Cloning, nucleotide sequence, and expression of the Bacillus subtilis lon gene. J Bacteriol. 1994;176(21):6518–6527.
Barkad MA, Bayraktar A, Doruk T, Tunca S. Effect of lon protease overexpression on endotoxin production and stress resistance in Bacillus thuringiensis. Curr Microbiol. 2021;78(9):3483–3493.
Charoensuk K, Irie A, Lertwattanasakul N, Sootsuwan K, Thanonkeo P, Yamada, M. Physiological importance of cytochrome c peroxidase in ethanologenic thermotolerant Zymomonas mobilis. J Mol Microbiol Biotechnol. 2011;20(2):70–82.
Hayashi T, Kato T, Furukawa K. Respiratory chain analysis of Zymomonas mobilis mutants producing high levels of ethanol. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2012;78(16):5622–5629.
Moreau RA, Powell MJ, Fett WF, Whitaker BD. The effect of ethanol and oxygen on the growth of Zymomonas mobilis and the levels of hopanoids and other membrane lipids. Curr Microbiol. 1997;35(2):124–128.

Published:
License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
